Reducing Load Times in Ruby on Rails Applications with Rails Caching Techniques
Learn how to reduce load times, improve performance, and scale your app using effective rails caching techniques.

Table of Contents
Have you ever noticed how frustrating it is to wait for a website to load?
Although the average mobile web page usually requires around 15 seconds to fully load, research from Google shows that an alarming 53% of users will abandon a mobile website if it exceeds the three-second loading mark.
For developers and business owners, this delay translates to missed opportunities, lower conversions, and unhappy users.
Caching is a solution to this problem!
It temporarily stores frequently used data so your application can retrieve it quickly without recomputing it every time.
This article explains how Rails caching techniques improve user experience and performance.
You’ll learn how to use caching effectively in your Ruby on Rails applications.
Key Takeaways
- Using Rails caching to store frequently accessed data for quick access can reduce load times, improve scalability, and enhance user experience. This approach can also help keep users on your site and increase conversion rates.
- Rails offers different caching methods, such as Page Caching, Fragment Caching, and Low-Level Caching. You can choose the best method depending on whether your content is static or dynamic.
- By saving query results, Rails caching reduces unnecessary database calls, which lessens the load on the database and improves response times, scalability, and overall system performance.
- Fragment Caching is useful for storing reusable components like headers or footers. Russian Doll Caching allows for nesting caches, ensuring that updates can occur without regenerating entire pages.
- For larger applications, dedicated caching tools like Redis or Memcached can greatly enhance performance by distributing cache across multiple servers, ensuring consistent data access even during high traffic.
What is a caching mechanism?
Imagine a student bookmarking a frequently referenced textbook page instead of flipping through the entire book each time.
Similarly, caching stores frequently used data so your application can quickly retrieve it without repeated searches.
This simple technique significantly speeds up your app, especially under heavy user traffic.
Why Use Rails Caching?
Rails caching stores frequently used data for quick retrieval, thus improving website performance and reducing loading times. This leads to increased user satisfaction, decreased server workload, and overall enhanced application speed.
Below are its key benefits.
Reduced Database Load
Rails caching, including the use of app cache, temporarily stores frequently accessed data, reducing the need to query the database repeatedly.
Faster Response Time
Cached data speeds up page load times, ensuring a smooth user experience. Faster websites improve customer satisfaction and reduce bounce rates.
Improved Scalability
Caching enables your application to handle more users simultaneously. Your website stays reliable during high-traffic peaks.
Better User Experience
A fast-loading application creates a seamless experience for users, encouraging them to stay longer and interact with your content. Positive user experiences lead to higher customer retention and increased conversions.
Improved Performance
Caching minimizes redundant computations, such as regenerating the same content multiple times. This optimizes your application’s overall performance and makes it more efficient.
Faster processing ensures smoother operations and better satisfaction for end-users.
Reduced Server Load
By reusing cached data, your servers perform fewer operations, leading to lower CPU and memory usage. This reduces the need for additional infrastructure, cutting costs while maintaining high performance.
Cost Optimization
Reducing server workload cuts infrastructure expenses. Backed by Rails caching, you can save money on hosting without sacrificing performance.
Ruby on Rails is one of the most trusted frameworks for building web applications. How to get the most out of it? You need the right Ruby on Rails hosting provider!
Types of Caching in Rails
Rails supports various caching methods tailored to specific application caching needs.
Page Caching
Page caching, which has been removed from Rails core and is now available exclusively through a gem like actionpack-page_caching, saves the entire content of a webpage.
This makes it ideal for static pages such as “About Us” or “Contact.” When a user requests one of these pages, Rails serves the cached version without regenerating it.
Business Benefit: Speeds up load times for non-dynamic content, reducing server processing.
Action Caching
Action caching stores the output of specific controller actions but allows for user-specific variations. It’s useful for pages with the same layout, but content differs for logged-in or logged-out users.
Business Benefit: Ensures personalized responses with improved speed.
Low-Level Caching
Low-level caching directly stores and retrieves raw data from the cache, bypassing Rails helpers. It’s suited for custom caching needs.
Example:
Rails.cache.fetch(“raw_data_key”, expires_in: 6.hours) do
SomeExpensiveComputation.call
end
Business Benefit: Grants full control over cached content and enables unique use cases.
SQL Caching (A Specific Case of Low-Level Caching)
SQL caching is a form of low-level caching that stores the results of database queries. Subsequent identical queries can retrieve the data directly from the cache instead of executing the query against the database again.
This approach significantly reduces the load on the database and improves application performance, especially under heavy traffic conditions.
Example:
Rails.cache.write(“query_results”, query_results)
Business Benefit: Minimizes the database workload, leading to faster response times and enhanced scalability.
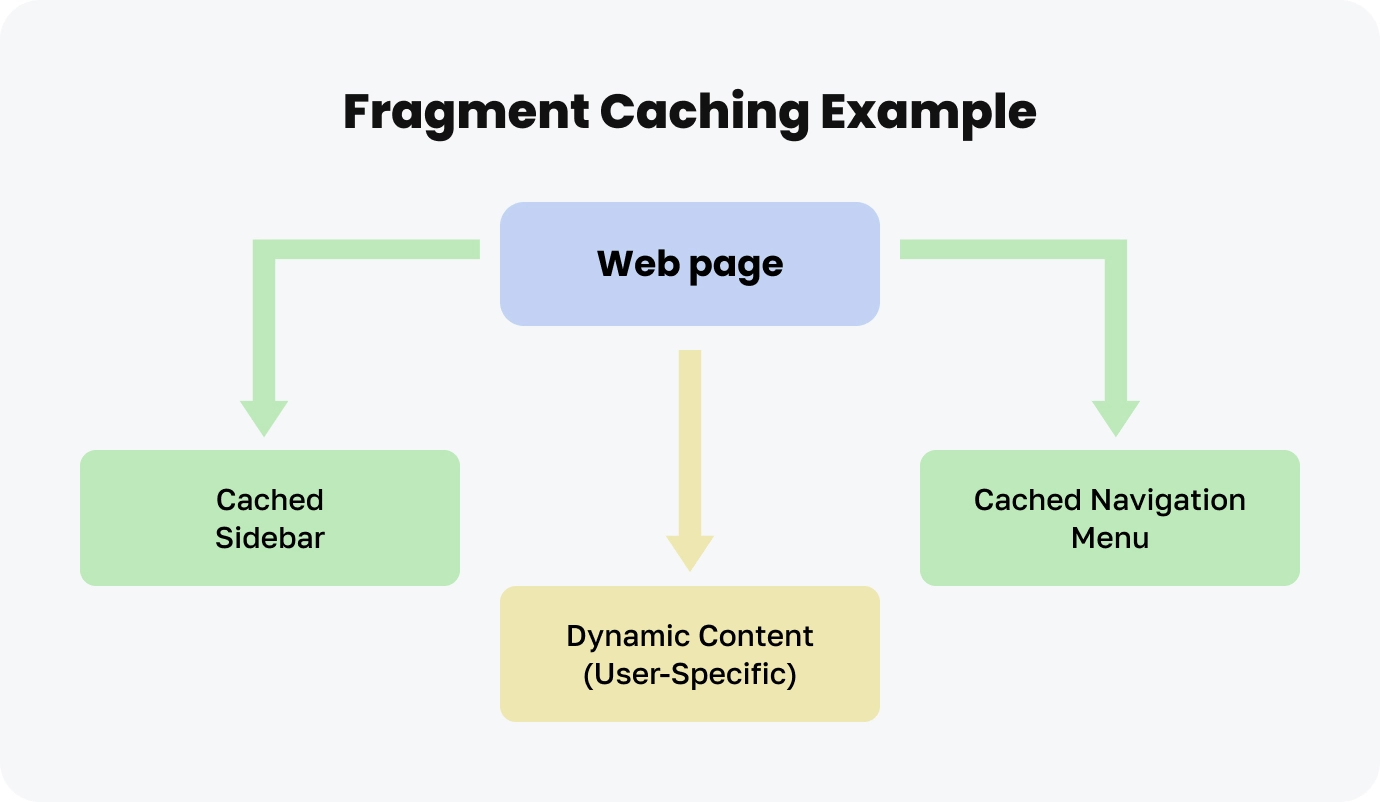
Rails Fragment Caching
Fragment caching stores reusable parts of a page, like headers, footers, or sidebars, while dynamic sections can still be updated independently.
Example:
<% cache [@article, “comments”] do %>
<%= render @comments %>
<% end %>The diagram below shows how Rails fragment caching optimizes webpage performance:
Business Benefit: Improves performance for pages with both static and dynamic components.
Russian Doll Caching
Russian doll caching builds on fragment caching by allowing nested caches. For example, a product detail page might cache product information and individual components like price or reviews as separate nested fragments.
Example:
<% cache [@product] do %>
<%= render “details”, product: @product %>
<% cache [@product, “price”] do %>
<%= render “price”, product: @product %>
<% end %>
<% end %>
Business Benefit: Saves resources by rebuilding updated fragments, not the entire page, thus optimizing the caching mechanism.
Shared Partial Caching
This technique allows caching reusable components that are shared across multiple pages, such as a “Featured Products” section displayed on the homepage and product category pages like “Portfolio” or “Case Studies”.
Example:
<% cache “shared_partial_key” do %>
<%= render “shared/featured_products” %>
<% end %>
Business Benefit: Reduces redundancy and enhances page load consistency.
Rails Caching Stores
Ruby on Rails supports multiple caching stores to handle data efficiently.
The cache store holds cached data for easy use. It can be in memory, in external files, or in other places, depending on the type of store used. This storage is important for making applications run faster.
Memory Store
A high-speed, in-memory solution for temporary caching. It enables quick access to frequently used data, enhancing performance by reducing the need for slower traditional storage.
Ideal for applications requiring rapid data retrieval, it ensures your information is readily available when needed.
Rails File-Cache Store
Saves cache data as files on the server, balancing speed and persistence.
Both Memory Store and Rails File Cache Store can cause problems in a multi-server setup because the cache is not shared.
Each server has its own cache, which can lead to outdated or inconsistent data. As a result, users may receive different information from different servers, creating confusion and unreliable experiences.
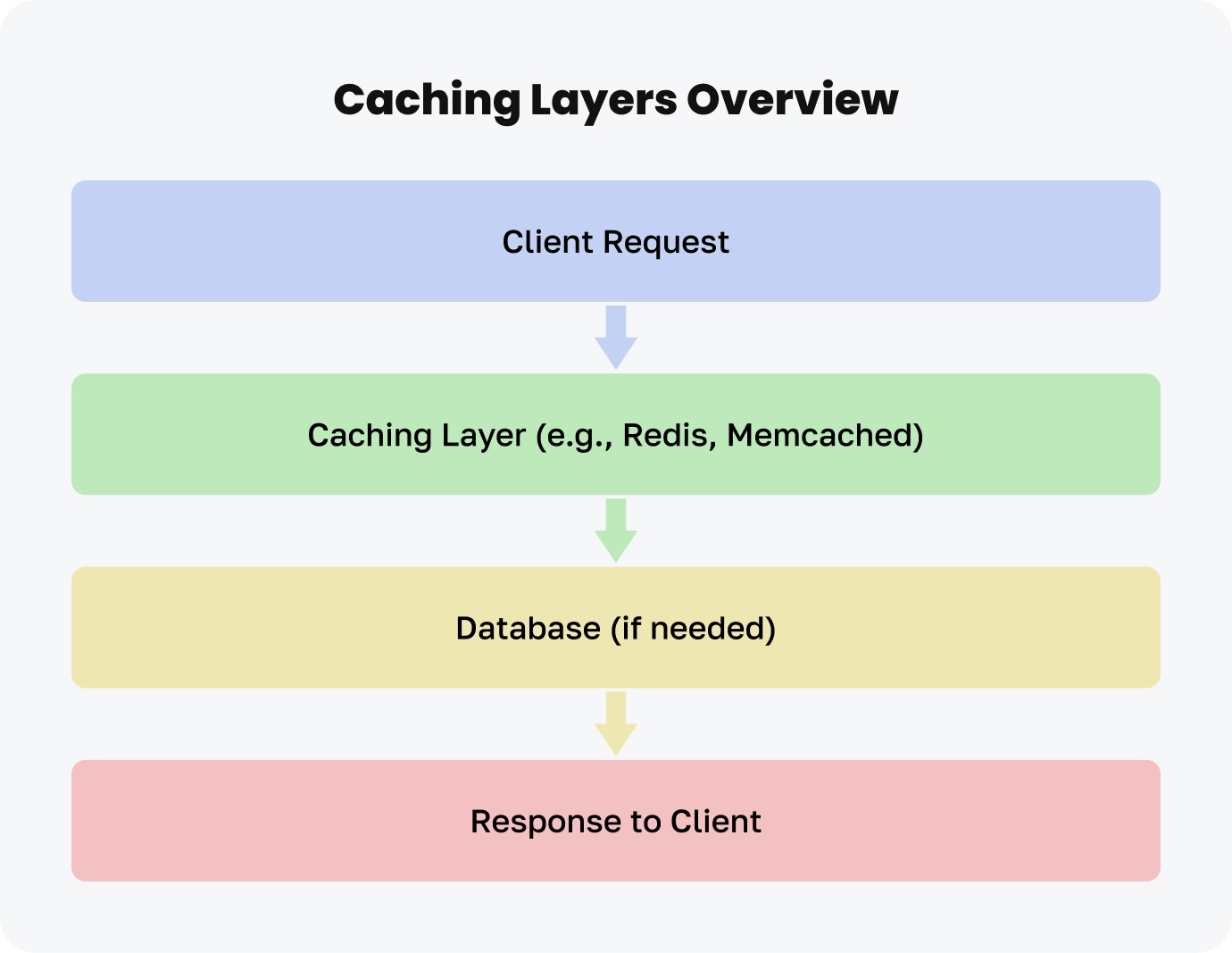
Rails Memcached Store
A distributed and scalable system that can handle a lot of users at the same time. It is reliable and can grow to meet the needs of high-traffic websites.
This makes it a good choice for improving performance in web applications.Example:
config.cache_store = :mem_cache_store, “cache-1.example.com”, “cache-2.example.com”
Redis Store
Redis Store is a caching system for Rails. It provides helpful features like data storage and support for complex data types.
These features make it a good option for applications that need improved performance and advanced data management.
Example:
config.cache_store = :redis_cache_store, { url: “redis://localhost:6379/0” }
Here’s a diagram illustrating how caching layers work:
Plans don’t always work out. A startup pivoting approach means recognizing this and being willing to change. How do you know when it’s time to pivot?
Implementing Caching Techniques in Ruby on Rails
Identifying the right caching strategies means choosing the right types, such as fragment, page, or SQL caching.
So, how to reduce load times and server strain using Rails’ caching directives?
Let’s uncover best practices for cache expiration, cache busting, and advanced layers like Redis and Memcached.
Identify the Right Caching Strategy
Before applying caching, analyze your application’s performance to pinpoint bottlenecks.
For example:
- Are database queries slowing down specific pages?
- Do users frequently access particular data or pages?
Tip: Use tools like New Relic or Skylight to monitor performance and identify areas where caching would have the most impact.
Leverage One of the Caching Types
Choose the most suitable caching type for your use case:
- Use Fragment Caching for reusable components like sidebars or navigation menus.
- Use Page Caching for static pages that rarely change.
- Use SQL Caching for frequently executed database queries.
Example:
<% cache [@article, “comments”] do %>
<%= render @comments %>
<% end %>
Use Caching Directives
Rails offers specific directives to control caching within your application, distinguishing between view-level caching and direct cache operations:
cache: Used within views to cache particular sections of a page. This is ideal for parts of the UI that do not change frequently, such as headers or footers.
<% cache do %>
<!– Expensive view code here –>
<% end %>
fetch: Used for caching the results of data queries. This directive retrieves data from the cache if available. Otherwise, it executes the query and stores the result in the cache for future requests.
Rails.cache.fetch(“query_results”) do
perform_expensive_query
end
write: Allows you to save data to the cache store explicitly. This is useful when you need precise control over what is cached and when it is updated.
Rails.cache.write(“key”, value)
By appropriately leveraging these caching directives, you can optimize view rendering and data retrieval efficiency, enhancing the overall performance of your Rails application.
Expire Caches When Needed
Cached data becomes outdated over time. Use expiration rules to refresh the cache automatically:
- Set expiration times for frequently changing data.
- Trigger manual expiration for specific events (e.g., product price changes).
Example:
Rails.cache.delete(“products”)
Business Impact: Expiring old cache ensures that users always see the latest updates.
Clear Rails Cache
Manually clear caches during development or for debugging:
- Use Rails.cache.clear to remove all cached data.
- Target specific keys with Rails.cache.delete(“key_name”).
Example:
Rails.cache.clear
Implement Cache Busting
Cache busting ensures that users see the latest version of your application when updates are made:
- Use versioning in file names (e.g., styles-v2.css) to signal changes.
- Add timestamps or unique keys to cache entries for dynamic data.
Example:
Rails.cache.fetch(“product_#{product.updated_at}”) do
product.details
end
Tip: Cache busting is particularly useful for static assets like JavaScript or CSS files.
Consider Using a Caching Layer
For high-traffic applications, integrating a dedicated caching layer like Redis or Memcached significantly improves performance:
- Redis: Ideal for advanced caching strategies requiring persistence and data structures.
- Memcached: Perfect for distributed, high-speed caching.
Example (Redis caching):
config.cache_store = :redis_cache_store, { url: “redis://localhost:6379/0” }
Example (Memcached):
config.cache_store = :mem_cache_store, “cache-1.example.com”, “cache-2.example.com”
Developers often spend too much time dealing with the same issues. This takes their focus away from solving larger problems. Find out how using AI in code review can help with this.
Leverage Ruby on Rails Caching with JetRuby
At JetRuby, we understand how frustrating slow or unresponsive web applications can be.
Your users expect speed, and delays can drive them away. That’s why we help businesses build high-performing applications that delight users.
Backed by over 15 years of expertise in Ruby on Rails and dozens of successful projects, our seasoned developers maximize caching’s potential to boost your app’s performance. Whether you have an existing application or need a new solution, we tailor our approach to fit your unique business needs.
We don’t believe in one-size-fits-all — our goal is to create a product that aligns perfectly with your objectives and grows with your business.
Flexible Solutions for Every Business
We offer a service called Staff Augmentation that provides highly skilled Ruby on Rails developers when your team is stretched thin.
Instead of hiring new employees, which can be time-consuming and costly, you can “borrow” our professionals who work well together and are ready to join your project in 2-3 weeks.
Here’s what makes our Staff Augmentation service special:
- A cohesive team, not just individuals: You get developers who are used to working as a group. This means they adapt quickly to your project and don’t waste time getting up to speed.
- Detailed updates: We provide clear monthly reports that show exactly what each developer has worked on. You’ll always know how your resources are used.
- Scalability: If your project grows or slows down, you can adjust the size of your team. Adding or reducing developers is simple; we make these changes with just one month’s notice.
This service is ideal for businesses that need to quickly expand their team and face challenges that their current staff can’t handle at the moment.
If you have any questions left or you need additional advice, please don’t hesitate to contact us anytime you see fit.